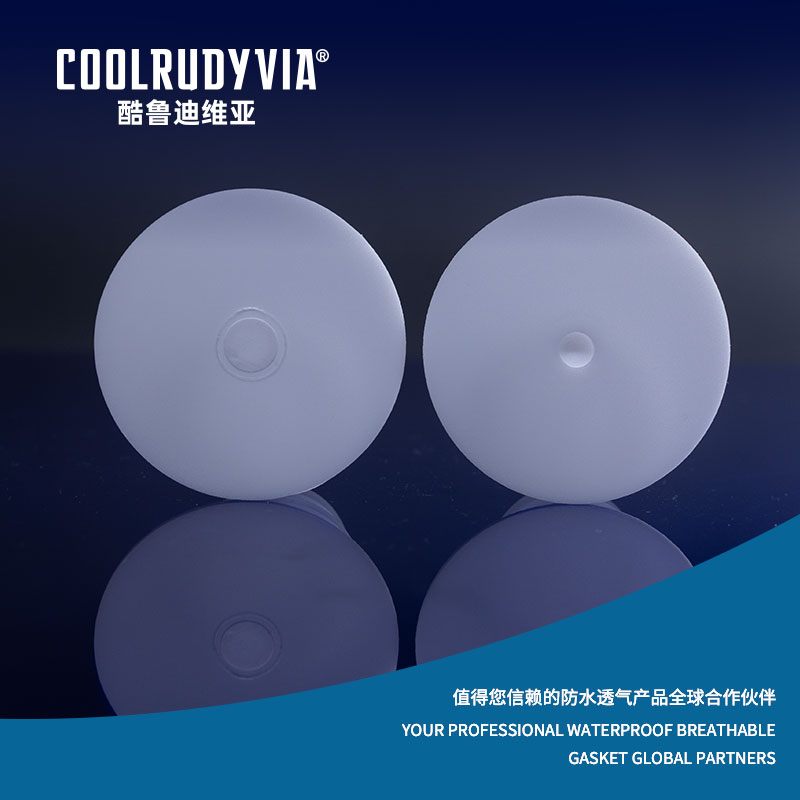
What Are Aluminum Foil Breathable Gaskets and Why Are They Important for Modern Industries?
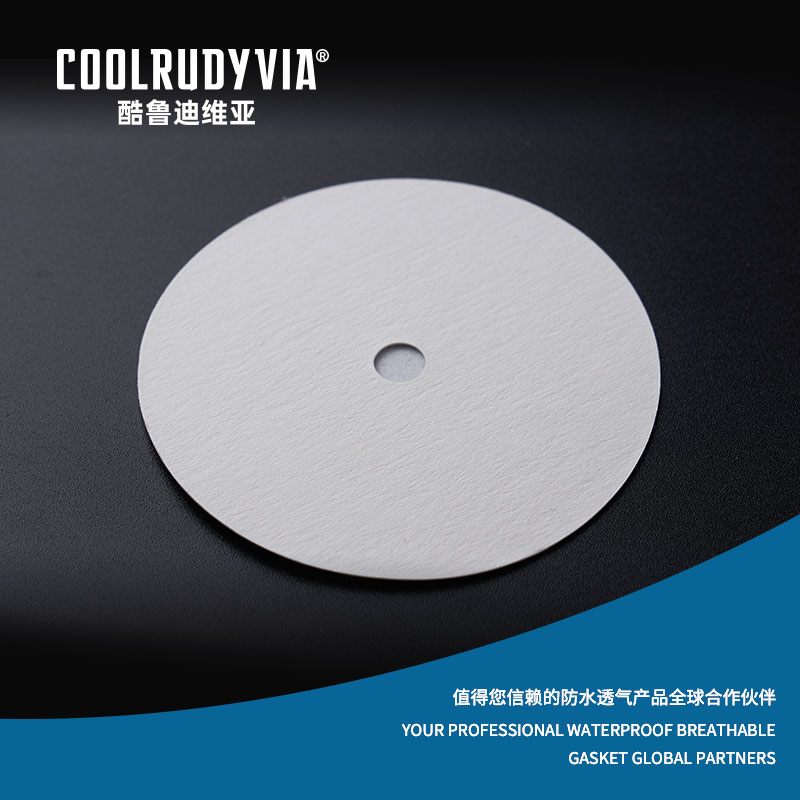
Aluminum foil breathable gaskets have become an essential component in a variety of industrial applications due to their unique combination of properties: being both breathable and waterproof. These gaskets are used primarily to prevent the ingress of moisture while allowing air or gases to pass through, which is crucial for maintaining the functionality and safety of numerous products.
Understanding Aluminum Foil Breathable Gaskets
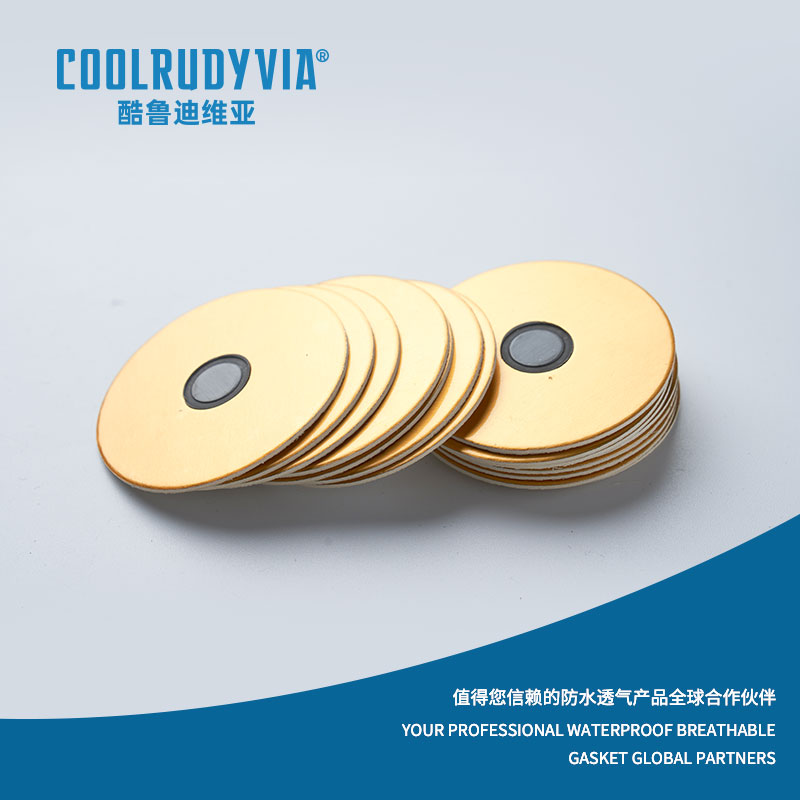
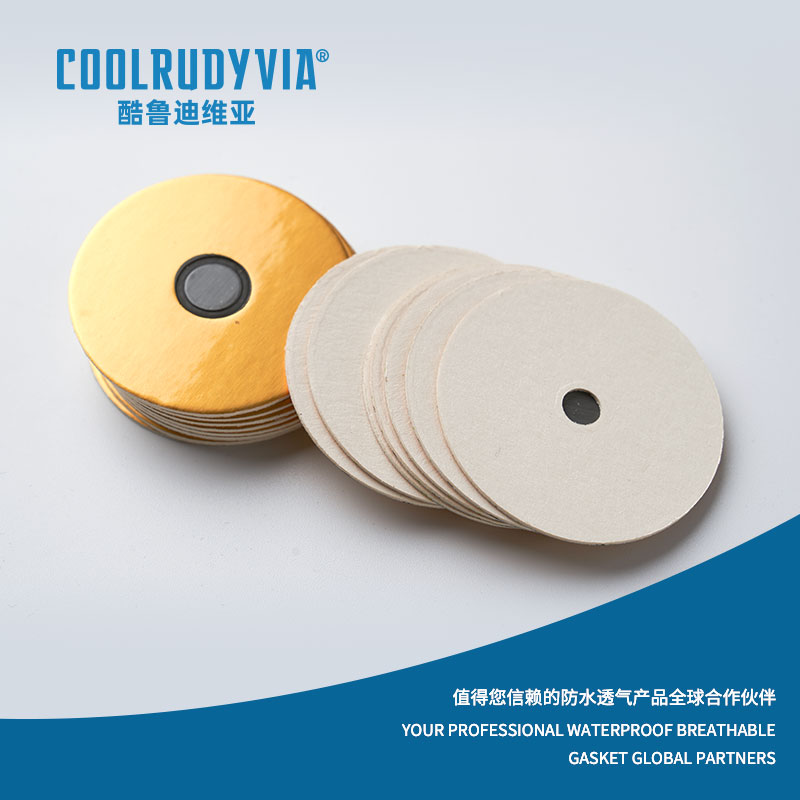
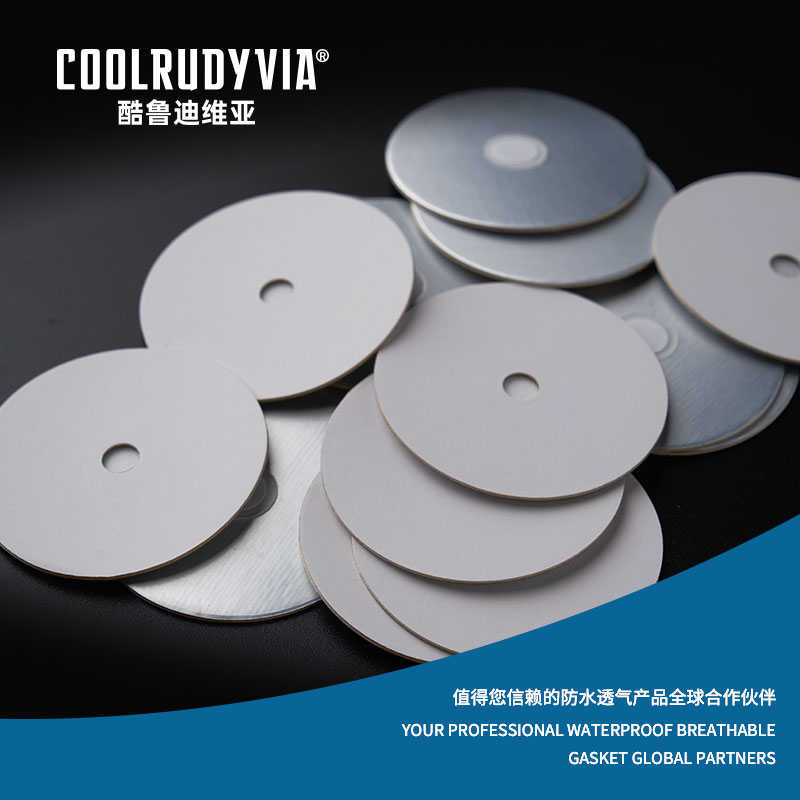
At their core, breathable aluminum gaskets are advanced sealing products made from aluminum foil, designed to protect sensitive equipment and products from moisture and contaminants, while allowing the controlled passage of air or gases. The unique design of these gaskets allows them to serve two vital functions:
- Waterproofing: The aluminum foil provides an excellent barrier to water, ensuring that moisture does not interfere with the integrity of the product or machinery it seals.
- Breathability: Despite their waterproof nature, these gaskets are engineered to permit air or gases to pass through. This feature is particularly crucial for applications in environments where the products need to “breathe,” such as in packaging that requires moisture control or automotive parts where ventilation is necessary to avoid condensation buildup.
Key Applications of Aluminum Foil Breathable Gaskets
Automotive Industry:
In the automotive sector, aluminum foil breathable gaskets are primarily used in automotive headlamps and electrical components. These gaskets help maintain the stability of the electrical systems in headlamps by preventing moisture from entering while allowing heat and gases to escape. This ensures that the lighting systems function optimally under varying weather conditions.
Packaging Industry:
Another significant use of aluminum foil breathable gaskets is in packaging. For products such as beverages and pesticides, ensuring the right level of moisture control is critical. These gaskets prevent the buildup of internal pressure while allowing the contents to “breathe,” thus preserving the integrity of the product without compromising its safety. The combination of waterproofing and breathability ensures that packaging remains intact during transportation and storage, preventing spoilage or degradation of the product.
Pesticide and Chemical Packaging:
In pesticide and chemical packaging, aluminum foil breathable gaskets are used to ensure the safe transport and storage of hazardous substances. The gaskets provide a reliable barrier against water and contaminants while facilitating gas exchange. This is particularly important for preventing chemical reactions that could be triggered by excess moisture or the inability of gases to escape.
Benefits of Aluminum Foil Breathable Gaskets
- Durability and Reliability:
The aluminum foil used in these gaskets is not only durable but also resistant to environmental factors like temperature fluctuations, humidity, and chemicals. This durability ensures that the gaskets can withstand the harsh conditions they are exposed to, whether in automotive systems or packaging environments.
- Enhanced Safety:
Aluminum foil breathable gaskets contribute to enhanced safety by preventing water ingress in sensitive applications. For instance, in automotive headlamps, the gasket ensures that moisture does not damage the electrical components, preventing potential malfunctions that could lead to accidents. Similarly, in packaging, these gaskets help maintain the safety of the product by controlling moisture and gas exchange, reducing the risk of contamination.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
These gaskets offer long-term cost savings by extending the lifespan of the products they protect. By preventing damage caused by moisture or pressure buildup, breathable aluminum gaskets help reduce the frequency of product replacements and maintenance, ultimately saving costs for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Why Choose Baonong Material?
Changzhou Baonong New Material Technology Co., Ltd. has become a leader in the design, R&D, production, and sales of waterproof and breathable products, including breathable aluminum gaskets. With over 90 sets of independent, high-speed automated equipment, the company ensures that each product is manufactured to the highest standards of precision and reliability. The integration of design and manufacturing capabilities allows Baonong to provide customers with tailored solutions that meet the specific requirements of industries such as automotive and packaging.
Baonong's commitment to quality is reflected in its dual inspection system, which involves both automated testing and manual inspections. This rigorous quality control process guarantees that each gasket performs optimally, offering both breathability and waterproofing. Whether for automotive headlamps or packaging solutions, Baonong's products are trusted by industries worldwide to deliver safe and effective results.
Conclusion
Aluminum foil breathable gaskets play a crucial role in a wide range of industries by providing the necessary protection against moisture and contaminants while allowing controlled gas exchange. From automotive headlamps to beverage packaging, these gaskets are indispensable in ensuring product safety and performance.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى